What is endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms?
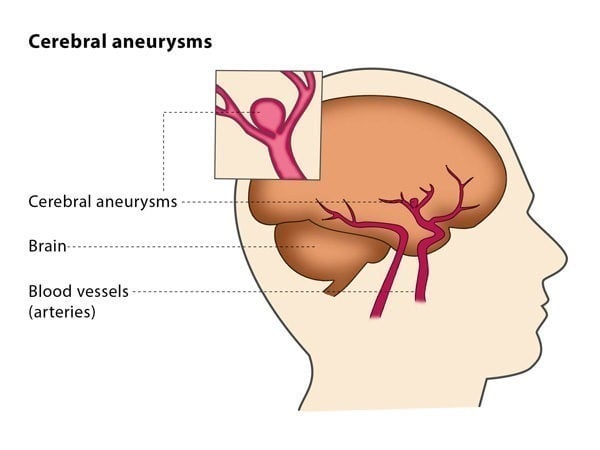
An aneurysm is an outward bulging of a blood vessel wall due to a weakness in the wall of a blood vessel. This causes the blood vessel to swell. When an aneurysm develops inside the brain, it is called an intracranial aneurysm. Depending on their size, intracranial aneurysms are associated with a high risk of bleeding in and around the brain, which can have catastrophic consequences. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms is the non-surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms using microcatheters (small and flexible plastic tubes) and X-ray guidance.
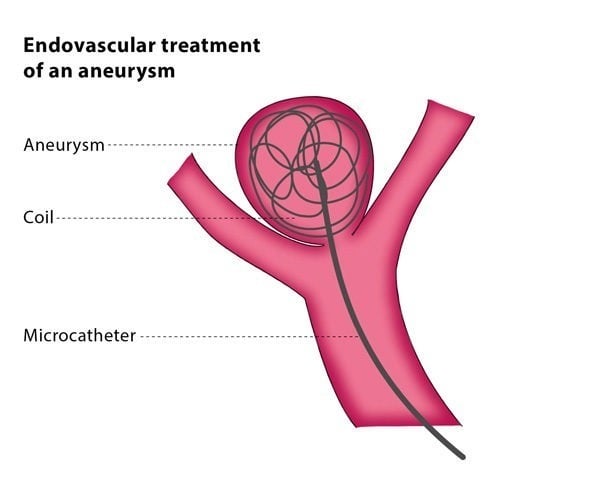
The procedure involves inserting tiny metal spirals (coils) into the blood vessel to act as a physical barrier and encourage blood clotting, preventing bleeding. A metal mesh tube (stent) may be used to keep the coils in place and support the walls of the blood vessel. Sometimes only stents are used without coils to change the blood flow and encourage clotting in the aneurysm. A special typeof stents calledflow diverters redirect blood flow without blocking side branches originating from the aneurysm.