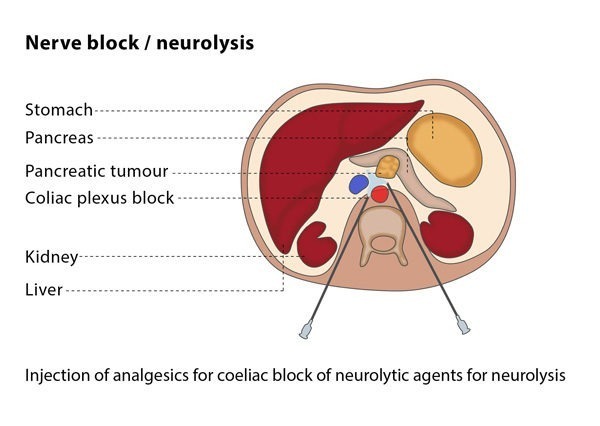
What are neurolysis, nerve block and plexus block?
Neurolysis is the deliberate destruction of a nerve or a network of interlacing nerves (plexus) with the aim of providing permanent relief from pain by interrupting the transmission of pain signals in the nerves.
Nerve block refers to temporarily blocking the function of a nerve by injecting anaesthetics and/or steroids into the area around the affected nerve, thus blocking/attenuating the transmission of pain signals. This temporarily disables the nerve without causing permanent damage.
How does the procedure work?
If you are undergoing neurolysis, there are a number of techniques which the interventional radiologist may use. The most common method of causing permanent nerve destruction is the injection of a chemical such as alcohol. Alternately, the interventional radiologist may choose to use thermal ablation techniques to destroy the nerves. In these cases, the interventional radiologist will insert a thermal probe into the area so it is in contact with the nerve or the plexus to destroy the target nerve with heat- or cold- based ablation techniques
If you are having a nerve block, the interventional radiologist will use a single thin needle to inject anaesthetics (sometimes mixed with anti-inflammatory drugs) into the area around the nerves responsible for pain.